Gabi Laske is a professor of geophysics on the College of California—San Diego.
Hawaii's Mauna Loa, the world's largest energetic volcano, started sending up fountains of glowing rock and spilling lava from fissures as its first eruption in almost 4 many years started on Nov. 27.
The place does all that lava come from?
We requested Gabi Laske, a geophysicist on the College of California-San Diego who led one of many first initiatives to map the deep plumbing that feeds the Hawaiian Islands' volcanoes, to elucidate.
The place is the magma surfacing at Mauna Loa coming from?
The magma that comes out of Mauna Loa comes from a collection of magma chambers discovered between about 1 and 25 miles (2 and 40 km) under the floor. These magma chambers are solely short-term storage locations with magma and gases, and aren't the place the magma initially got here from.
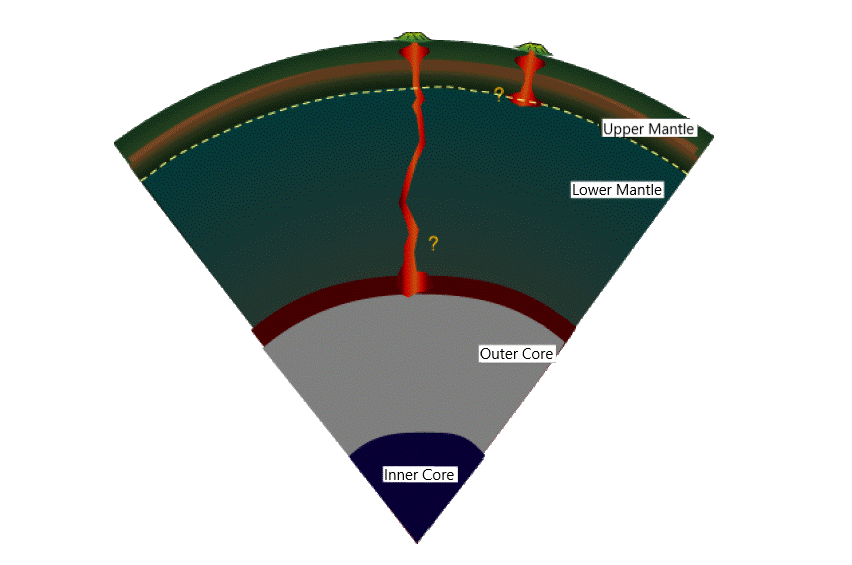
The origin is far deeper in Earth's mantle, maybe greater than 620 miles (1,000 km) deep. Some scientists even postulate that the magma comes from a depth of 1,800 miles (2,900 km), the place the mantle meets Earth's core.
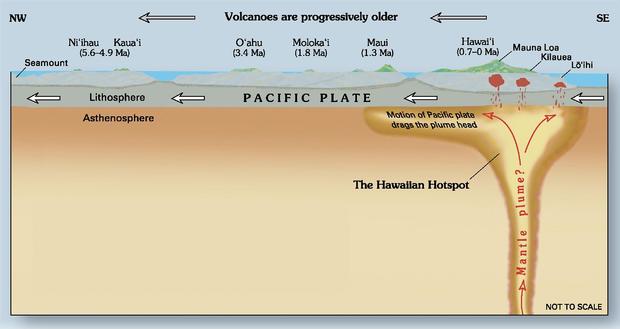
Earth's crust is made up of tectonic plates which might be slowly transferring, at about the identical velocity as a fingernail grows. Volcanoes usually happen the place these plates both transfer away from one another or the place one pushes beneath one other. However volcanoes will also be in the course of plates, as Hawaii's volcanoes are within the Pacific Plate.
The crust and mantle that comprise the Pacific Plate cracks at totally different locations because it strikes northwestward. Beneath Hawaii, magma can transfer upward via the cracks to feed totally different volcanoes on the floor. The identical factor occurs at Maui's Haleakala, which final erupted about 250 years in the past.
How does molten rock journey from deep in Earth's mantle, and what precisely is a mantle plume?
Scientists hypothesize that the mantle is just not fabricated from uniform rock. As an alternative, variations within the sort of mantle rock make it soften at totally different temperatures. Mantle rock is stable at some locations, whereas it begins to soften at different locations.
The partially molten rock turns into buoyant and ascends towards the floor. The ascending mantle rock is what makes a mantle plume. As a result of the overlying stress lessens because the rock ascends, it melts increasingly more, and finally collects within the magma chamber. If a big sufficient opening exists on the floor, and sufficient volcanic gases have collected within the magma chamber, the magma is compelled to the floor in a volcanic eruption.
Seismic imaging by analysis groups I am concerned with has proven that Hawaii's mantle plume comes from deep contained in the mantle.
However the plume is just not a straight pipe as some idea figures counsel. As an alternative, it has twists and turns, initially coming from the southeast, however then turning towards the west of Hawaii because the plume reaches into the shallower mantle. Cracks within the Pacific Plate then channel the magma upward towards the magma chamber beneath the island of Hawaii.
Why does Hawaii usually see much less dramatic eruptions than different areas?
Hawaii is in the course of an oceanic plate. The truth is, it's the most remoted volcanic sizzling spot on Earth, distant from any plate boundary.
Oceanic magma could be very totally different from continental magma. It has a special chemical composition and flows far more simply. So, the magma is much less vulnerable to clog volcanic vents on its ascent, which might in the end result in extra explosive volcanism.
How do scientists know what is occurring beneath the floor?
Volcanic exercise is monitored with many various devices.
The maybe easiest to grasp is GPS. The best way scientists use GPS is totally different from that of on a regular basis life. It may well detect minuscule actions of some centimeters. On volcanoes, any upward motion on the floor detected by GPS signifies that one thing is pushing from beneath.
Much more delicate are tiltmeters, that are in essence the identical as bubble ranges that individuals use to hold footage on a wall. Any change within the tilt on a volcano slope signifies that the volcano is "respiration," once more due to magma transferring under.
A vital instrument is anticipating seismic exercise.
Volcanoes like Hawaii's are monitored with a big community of seismographs. Any motion of magma under will trigger tremors which might be picked up by the seismometers. A couple of weeks earlier than the eruption of Mauna Loa, scientists seen that the tremors got here from ever shallower depths, indicating that magma was rising and an eruption is perhaps imminent. This allowed scientists to warn the general public.
Different ways in which volcanic exercise is monitored embrace chemical evaluation of gases popping out via fumaroles – holes or cracks via which volcanic gases escape. If the composition modifications or exercise will increase, that is a reasonably clear indication that the volcano is altering.
This text is republished from The Dialog beneath a Artistic Commons license.